 |
||||
|
INSULTECH |
||||
|
Frequently Asked Questions About Sound 1. How do I add two or more sound levels? Sound levels, measured in dB, represent a logarithmic ratio which cannot simply be added or subtracted without lengthy calculations. To simplify this, follow the below chart: |
|||
|
Decibel Difference |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
Correction |
3.0 |
2.6 |
2.1 |
1.8 |
1.5 |
1.2 |
1.0 |
0.8 |
0.6 |
0.5 |
.04 |
|
Source: OSHA Appendix A - Section 1910.95 Noise Exposure Computation Adding two sound levels:
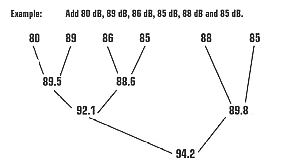
Example: 80 dB + 81 dB = 81 + 2.6 = 83.6 dB Adding multiple sound levels:
|
|||||
 |
|||||
|
Therefore, the overall sound level is approximately 94.2 dB. 2. Is a 7 dB overall reduction good? Since decibels represent a logarithmic ratio, the before and after sound pressure levels cannot be simply expressed as a percent reduction. The absolute reduction in dB, regardless of the levels, can be determined using the following chart: |
|||||
|
Sound Reduction (dB) |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
|
Absolute Reduction (%) |
11 |
21 |
29 |
37 |
44 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
64 |
68 |
82 |
90 |
|
3. Does sound pressure decrease with distance? As the distance between the source and the receptor increases, the sound pressure decreases. In fact, each time the distance is doubled, the sound intensity decreases by 3 dB. Please refer to the chart below to determine the sound level decrease. Also note that 3' away from the source is the standard measuring distance. |
|||
|
Distance from noise source |
3' |
6' |
12' |
24' |
48' |
|
Sound Reduction (dBA) |
0 |
3 |
6 |
9 |
12 |
|
4. What is the difference between dB and dBA? Decibels, abbreviated dB, are a logarithmic unit for expressing sound power and sound pressure levels. A-weighting this unit, referred to as dBA, adjusts the low and high frequency levels to more closely approximate the human ear's response to noise. This scale is based on a child's hearing. To convert dB to dBA, simply subtract the following corrections for each frequency using the following table: |
|||
|
Frequency (Hz) |
31.5 |
63 |
125 |
250 |
500 |
1000 |
2000 |
4000 |
8000 |
|
Correction |
-39.4 |
-26.2 |
-16.1 |
-8.6 |
-3.2 |
0 |
+1.2 |
+1.0 |
-1.1 |
|
|
|||||